Architectural Terms used on this site
|
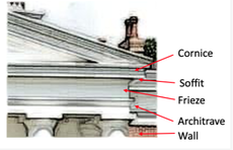
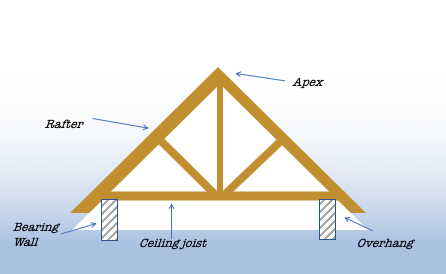
Adobe Bricks Adobe bricks date from the earliest times and are made from mud or clay then baked. Adobe walls are often covered in a sand and lime-based stucco Apex Pointed top of a gable or pediment Arcade A passage covered by arches which are supported by columns or similar Arch A curved or pointed structure spanning an opening that is supported at its sides. Architrave Moulded frame of a door or window or in earlier times a horizontal beam supported by columns Archway An opening with a pointed or curved top. Asymmetry A characteristic by which the two sides of a facade or architectural floor plan of a building do not present mirror images of one another. (see Symmetrical) Atrium Open roofed entrance or central court Balcony A projected platform often outside a window which is enclosed on the outer three sides by a railing, or parapet. Baluster A small pillar or column supporting rail. Balustrade A railing with small posts headed by a coping usually seen on stairs, or a roof. Bargeboard a board trim that is usually carved and projects from the gable line of a roof, used to hide the ends of the horizontal roof timbers. Bay Part of a building divided by vertical elements such as columns or pillars. Often, a bay will protrude from the surface of the wall in which it is situated, thus creating a small, nook-like interior space, often of a rectangular or semi-hexagonal outline. See bay window. Bay Window is a window space projecting from the face of the walls of a house forming a bay in a room. It has a straight frontage with angled sides and adds light to a room Beam Horizontal structural support Bell Roof A bell-shaped roof which sits on top of a round tower. Belvedere Most often in Italianate houses it is a small, square dome on the top of a house that provides light and ventilation plus a good view Bousillage A type of plaster formed by mixing mud, clay and moss, Found mainly in French Colonial buildings Bracket Projects from a wall and provides support beneath an eave or overhang. Can be ornamental. Buttress Brickwork or masonry that projects from the wall to provides support and often stability to the building. Often used to stabilise an arch or vault Canopy a projecting ornamental hood or cover Cantilever An unsupported overhang acting as a lever, like a flagpole sticking out of the side of a wall. Capital Decorated top of Classical column Casement Window A window frame hung on one vertical side which opens in or the out. Often in pairs Castellated Made to look like a castle with grooves or recesses that look like a battlements or turrets. Cladding Exterior covering of fascia Clapboard A type of wooden siding Colonnade A row of columns supporting arches Column A vertical support usually round which can be plain or ornamental. Cone-shaped Roof A roof shaped like a cone. Coping the capping or covering of a wall. Coquina A sedimentary rock composed either wholly or almost entirely of fragments of the shells of mollusc’s other invertebrates. Corbel Could be a bracket - is a structural piece of stone, wood or metal jutting from a wall to carry a weight, a type of bracket. Cornice a decorative projection along the top of a façade supported by brackets or corbels. In Classical architecture, the upper part of an entablature. Also known as a battlement is a row of alternating raised and lowered wall sections at the top of a high exterior wall or parapet such as on a castle. Cresting is a metal ornamentation on the roof ridge, coping or parapet, Cupola A small, most often dome-like, structure but sometimes hexagonal tower on top of a building. Decorative Motif A decorative element, theme or pattern often repeated. Common in in classical architecture Dentil Dentil is a series of small rectangular blocks or “teeth” adorning a cornice or interior moulding. Diamond-paned Windows Windows with small, diamond-shaped panes of glass, most common in Colonial and Colonial Revival buildings. Dormer Window A structure that extends outward from a roof, and contains a window. The dormer usually has a gable roof, but it may also be arched. Double Doors A pair of doors within one door frame, often referred to as “French doors” Double-hung Sash Windows A window with two sashes that move independently of each other. Drip Mould a moulded projection on an outside wall over an opening designed to throw off rainwater. See Hood mould, Dripstone Eaves the edge of a roof that extends /overhangs beyond the wall of the building protecting the wall from rain Facade The main front face of a building. Fanlight A window over a window or door. Often semi-circular or semi elliptical with glazing bars in a fan shape Fascia Board horizontally attached to the lower end of rafters at the eaves. Finial an ornamentation (ball) fixed to the top of an arch, gable or upright Flared Roof A roof in a bell-shape. The sloping roof has concave curves at the top and convex curves at the bottom. Fluting Shallow, vertical grooves in the shaft of a column or pilaster. French Doors Two adjacent doors that share the same door frame, and between which there is no separating vertical member. French doors are often referred to as “double doors.” Frieze generally, a horizontal band or strip on a wall or façade Gable the triangular end of an exterior wall above the eaves on a gable roof Gable Roof A roof that has two slopes front and rear meeting at a ridge leaving triangular end walls Gallerie A covered porch/hallway which wraps around the house. It has columns on one side, Gambrel A symmetrical two-sided roof with two slopes on each side. Gambrel Roof Ridged roof with two slopes, the lower slopes being steeper than the upper slopes. Gingerbreading Wooden architectural ornament often scalloped or zig-zag-edged clapboards, which were often painted in contrasting colors. Glazing Bar A horizontal or vertical bar that divides a pane of glass. Also called a Muntin Gothic window Seen mainly in churches these have three windows and the middle one is taller than the others Grilles Ventilation panels, sometimes decorative. Half-timbering A timber skeletal framework which is then filled with wattle & daub, masonry or plaster. Most frequently seen on Tudor style buildings Hipped Roof type of roof where all sides slope downwards (pitch) from the ridge to the eaves. Hood Is a section above a door that keeps rain off and is sometimes decorated Jack Arch. Provides structural support where there are openings in masonry. They consist of wedges of stone compressed together by the building process and are flat (not actually arched shape Jerkinhead roof a ridged roof with gable ends, in which the ends are sliced off to give the appearance of a fold or turndown. Jettied Story An upper part of a building projecting out over the floor beneath it |
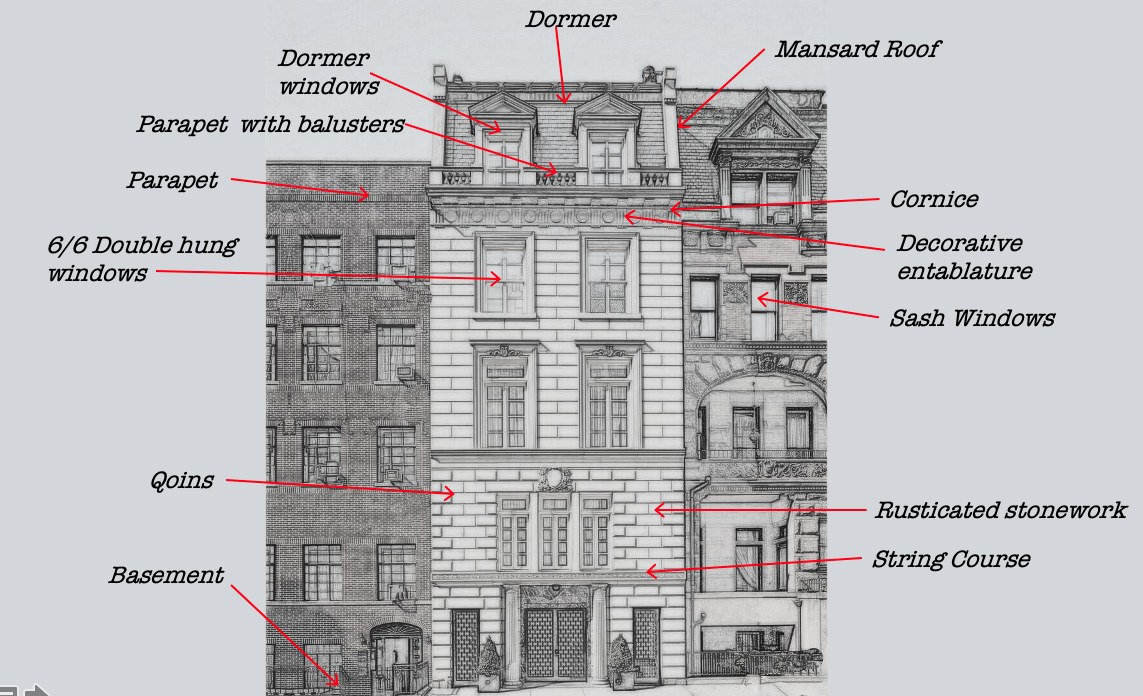
This French Revival Townhouse demonstrates the architectural features used in many house styles
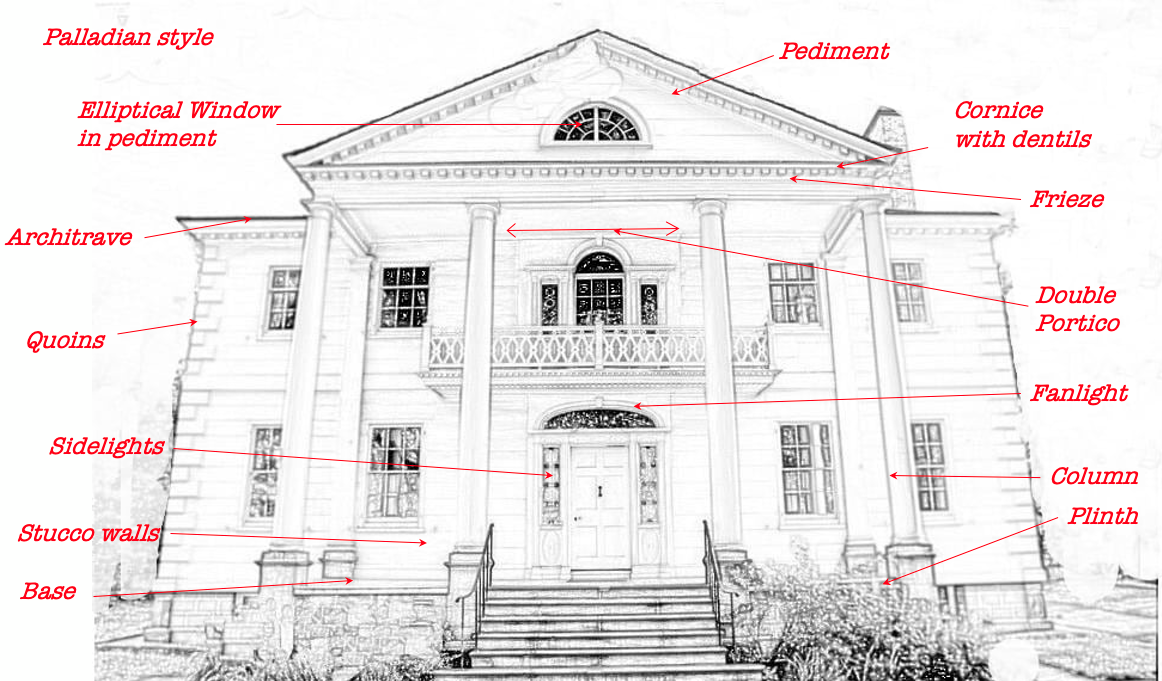
A Neo Classical Style house demonstrates some of the architectural terms used for many classic and revival styles
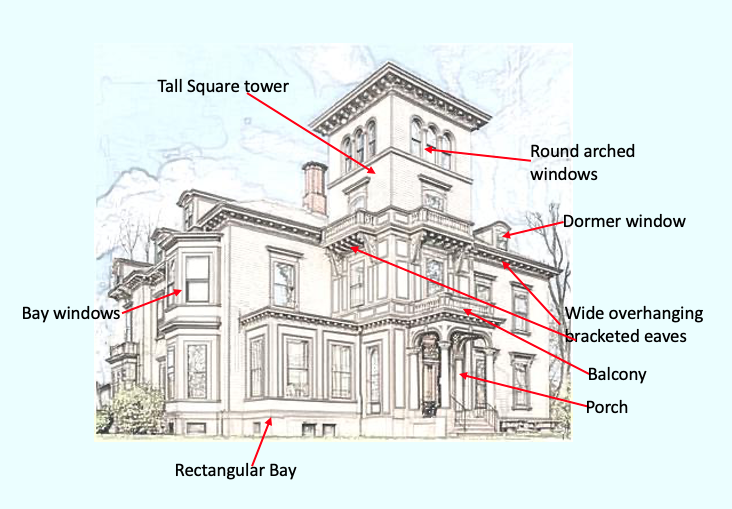
Features of an Italianate style house
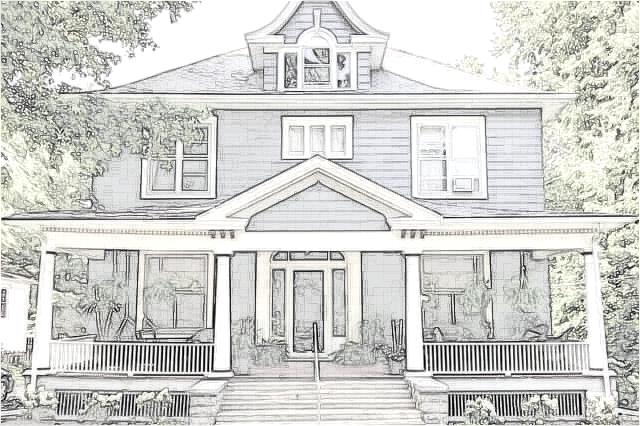
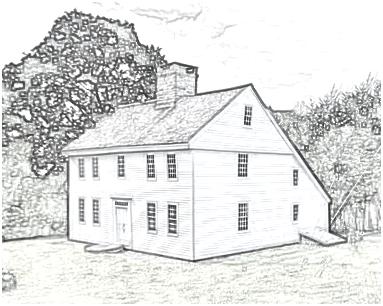
Asymmetrical Colonial Revival House with full width porch
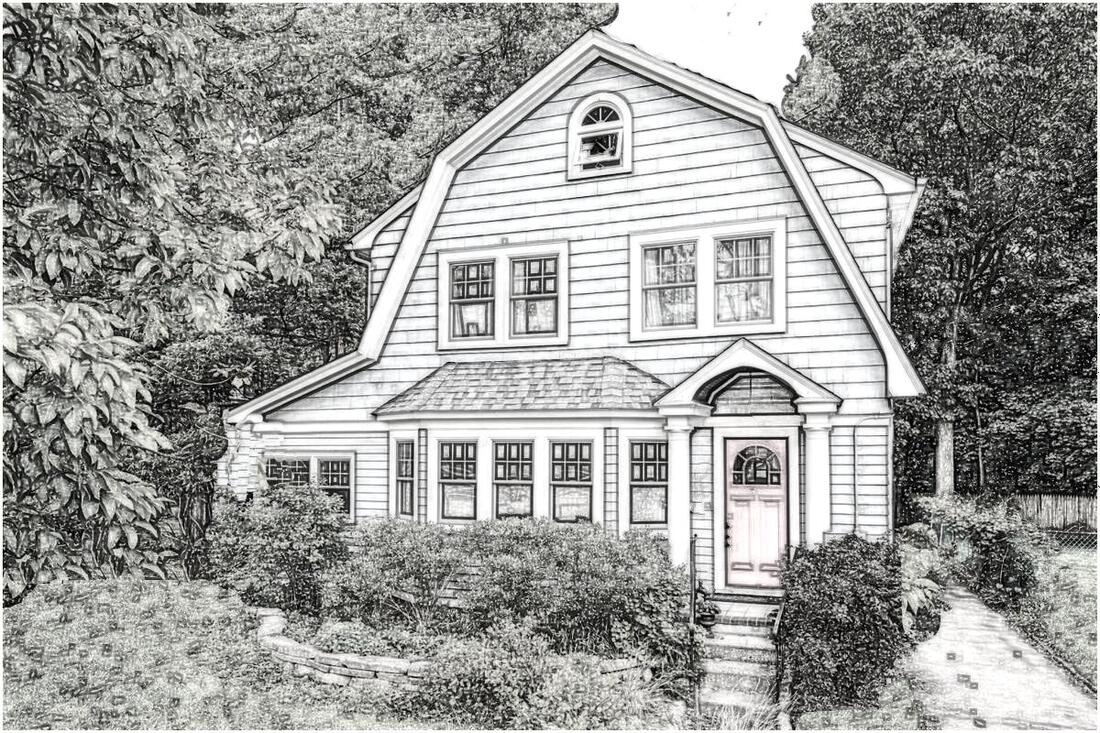
Dutch Colonial Revival house demonstrating a Gambrel roof
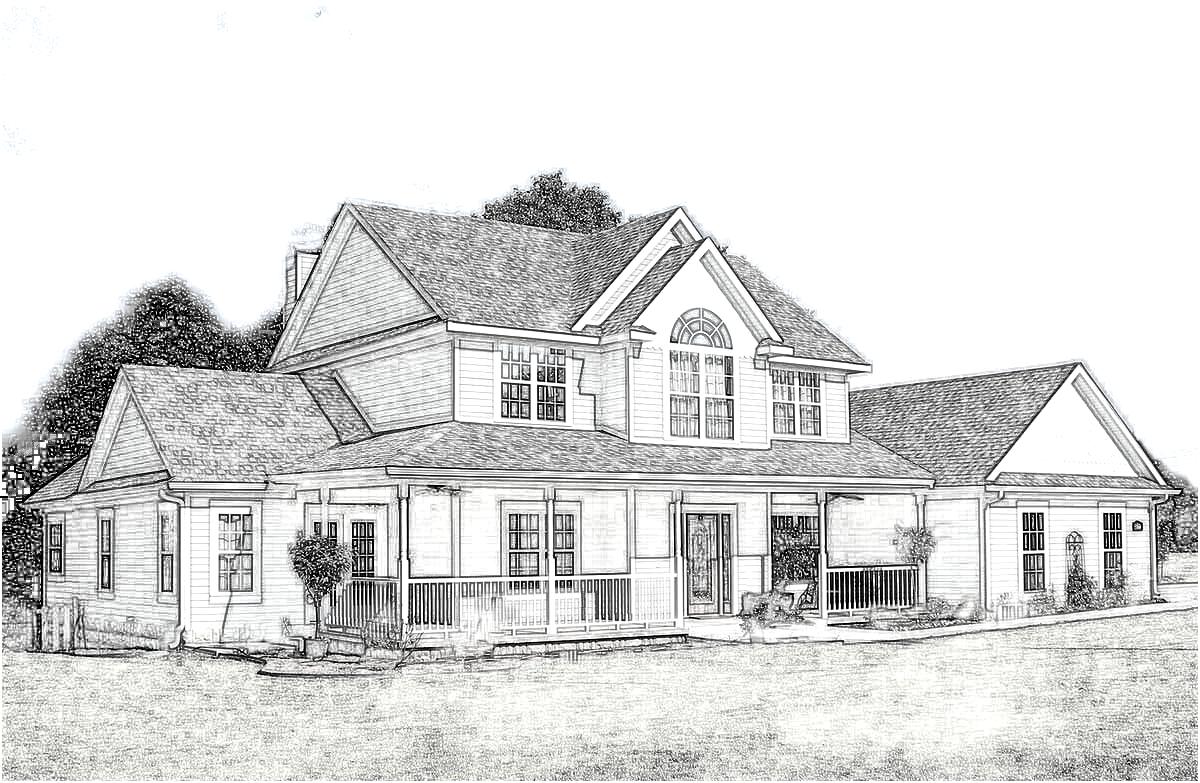
An example of a house with wings and mixed gables
|
|
Lattice-work. A wooden lattice frame of small strips of board overlaid on top an exterior surface. See stick-work.
Lintel. A horizontal block that spans the space between two supports usually over an opening such as a window or door. Mansard a very steeply sloped, straight, or concave roof that frequently is pierced with projecting dormer windows and sometimes with towers. The mansard roof is a key characteristic of the Second Empire style. Mansard Roof Four-sided hipped roof with two slopes each side the lower one steeper (almost upright) with a concave curve. Masonry Building material of stone, brick, or concrete. Molding A decorative strip of wood. Mullions Vertical bar made from wood, metal or stone which separates two or more windows Muntins A horizontal or vertical bar that divides a pane of glass.Also called a glazing bar Ogee Arch An arch consisting of a reverse curve meeting in a point at the apex. Oriel. A projecting bay window on an upper floor Over-hanging Rafters Rafters that extend beyond the eaves of a roof and overhang the walls. There by keeping the walls dry or in some cases providing cover. Palisade a wall made out of vertical poles set in to the ground often used as a defence Palladian a window in three parts where the centre is arched and wider than the two straight topped side windows. Palladian Window An arched window with two smaller, non-arched windows next to it. Parapet A low wall mainly around top of the facade of a building. Pediment a decorative triangular cap placed over a door or window supported by columns or pilasters The area within the triangular section is the “tympanum,” and is often decorated Pergola A garden structure consisting of evenly spaced columns or posts that support a wooden-framed roof Pilasters. a slightly projecting rectangular column incorporates a capital, shaft and base and is used mainly for common for decoration. Pillar Similar to a column, but of variable shape, such as rectangular (a four-sided pillar that widens toward its base) Pointed Arch An arch with two curves that end in a point in the centre Portico A covered area which has a colonnaded front usually a porch or covered walkway Post & Beam Is a construction process that uses heavy timbers See: timber framing Quatrefoil Four leaf shaped decorative element on buildings Quoins The corner stones at the junction of walls made from brick or stone walls. Often finished in different materials then the remainder of the building Rafters plate of the external wall and is usually set side by side to support the roof coverings Used in roof construction a rafter runs from the ridge or hip of the roof to the wall Roof Ridge Horizontal intersection of two roof slopes at the top of a roof. Round-arched Window Window fully arched at its top. Roundel Circular moulding Roundel A small, circular panel or window. Rusticated is a masonry technique giving visible surfaces a finish that contrasts in texture with the smoothly finished, squared-block masonry surfaces Saltbox Roof A gable roof where the rear slope is longer than the front slope sometimes reaching near to the ground. Sash One or more moveable frames in a window in which window panes are set. Setback A step-like recession in a wall. Shingle small, wooden tile Shiplap horizontal wooden siding with overlapping edges designed to protect stone and masonry exteriors Shutters Wooden (sometimes metal) hinged frame set either side of an external window which can be closed to cover the window. Within the frame you may find a solid or louvred finish Side Light A window positioned to the side of a doorway or window. Siding Siding is wall cladding protecting the exterior of a wall of a house See Single hung A window with a fixed top sash and a lower sash that slides vertically See sash Slate Is a strong and durable finely grained sedimentary rock used for roofing houses or sometimes cladding the outside Spandrel the triangular area between arch and its rectangular surround Spire A conical pyramid type structure which tapers towards the top and is often on a church. Stick-work A wooden lattice frame of small strips of board overlaid on top an exterior surface. See lattice work. Looks similar to a half-timbered frame building Striated Brick Rows of brickwork with alternating colors, typically red and white. Stucco A mix of sand and cement with sometimes stones used to coat walls to keep them waterproof (Also known as Render) Symmetrical Referred to in architecture as a building that is pleasing and has beautiful proportions. If the building were cut in half each side mirrors the other Terrace A terrace is a flat area outside the building usually raised and with a flooring of stone or other materials. It can also refer to a seating out area on a flat roof Transom Can be the window above a door but is also the horizontal beam between a door and a window above it Transom Light A narrow window, often hinged at the top and is found over a doorway or larger window. Truss Wooden or metal connected in a frame designed to support the structure usually the roof Turret A small tower above the roofline which is typically round and has a conical roof. Often seen in Medieval European castles Veranda An open, roofed area in front of the house sometimes wrapping round two or more sides and typically with balustrade or railings on the outside Window Sash One or more moveable frames in a window in which window panes are set. Wing Side part of a house Wooden Clapboards A traditional external weatherproofing method consisting long slats of wood nailed to the outside of the building horizontally, overlapping one another from top to bottom. Wooden Shingles A traditional external weatherproofing method consisting of small rectangular slats of wood which are fixed to the building and overlap each other |
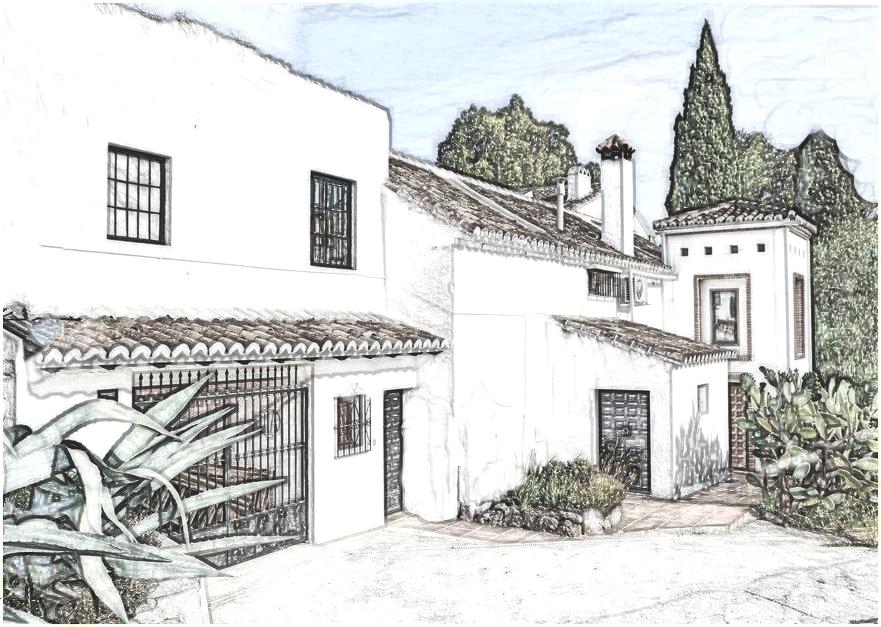
Spanish style house.Low pitched roof with little or no overhang. Red tile roof covering. Wall surface stucco
Half timbering Gothic style Victorian house with Gambrel roof
|
The HouseLand Registry
Maps Manorial Records Other Records Postcards & Photos Enclosures Books & House histories Church & Parish Records |
The People |
|
OUR ADVERTISING POLICY - This website receives no funding or any other form of award and is run voluntarily to provide information to those who want to trace the history of their house. We would like to say thank you to all those who have or will in future click on the advertisements they find on this page. We know they can be a nuisance or distraction and we try to make sure that they are relevant to the information we provide and our readers. However the modest income we receive from them keep the web site going. So thank you.